Data privacy has become increasingly important, and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is a significant step in this direction. It empowers California residents with more control over their personal information. As concerns grow, the CCPA provides transparency and essential rights, including data access, deletion, and the option to opt-out.
Despite this, many businesses face challenges in staying compliant. The risks of fines and reputational harm are significant. Compliance requires updating policies and managing data practices effectively.
You can become CCPA compliant simply and quickly by using the Seers CCPA Compliant Cookie Consent Solution.
What is the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)?
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is a significant legislation that enhances privacy rights and consumer protection for California residents. It marks a landmark shift in data privacy regulation in the U.S. The CCPA was signed into law on June 28, 2018, and became effective on January 1, 2020.
The purpose of the CCPA law is to give consumers more control over their personal data and ensure transparency in how their information is collected and used.
What Rights Does the CCPA Give to Consumers?
The CCPA gives consumers several rights, including knowing what personal data companies have collected about them, requesting deletion of their personal data, opting out of the sale of their personal information, and being protected from discrimination for exercising these rights.

- Right to Know:
Consumers can ask a business to tell them what personal data has been collected about them. The business must provide this information within 45 days. - Right to Deletion:
Consumers can request that their personal data be deleted. There are some exceptions, like when the data is needed for legal reasons or to complete a transaction. Businesses must also ensure that any service providers delete the data. - Right to Opt-Out:
Under Section 1798.120 of the CCPA, Consumers can choose not to allow their personal information to be sold. Businesses must include a “Do Not Sell My Personal Information” link on their website to make opting out easy. - Right to Non-Discrimination:
Consumers should not be mistreated for using their CCPA rights. This means businesses cannot deny services or charge higher prices because consumers exercise their rights.
Act Now Before It’s Too Late!

Seers will help you
- Navigate the complexities of the law
- Address any concerns
- Implement strategies to avoid penalties and protect your business.
How Does the CCPA Define ‘Personal Information’?
The CCPA broadly defines ‘personal information,’ covering various data types.
- Identifiers: Names, email addresses, and Social Security numbers.
- Commercial Information: Records of products or services purchased and other purchasing histories.
- Biometric Information: Fingerprints, voiceprints, and retina scans.
- Internet Activity: Browsing history, search history, and interactions with websites.
- Geolocation Data: GPS data and other location information.
“Definition of personal information is expansive and includes both online and offline data.”
California Department of Justice
Where Does the CCPA Apply?
The CCPA applies to certain businesses based on their operations and data processing activities.
The CCPA applies to for-profit businesses that collect personal data from California residents and meet at least one of the following criteria:
- Businesses with annual gross revenue over $25 million.
- Entities processing personal data of 50,000 or more consumers, households, or devices.
- Companies that derive 50% or more of their revenue from selling personal information.
Generally, the CCPA does not apply to nonprofit organisations or government entities.
Is CCPA Compliance the Same as GDPR Compliance?
While the CCPA and GDPR both focus on consumer privacy, they have important differences.
| Aspects | GDPR | CCPA |
| Geographic Scope | Applies to entities processing the personal data of EU residents | Applies to businesses dealing with California residents’ data |
| Rights And Protection | Provide comprehensive rights, including data portability and correction | Emphasises transparency and control over data sales |
| Penalties | Fines up to €20 million or 4% of global revenue, whichever is higher | Fines range from $2,500 per violation to $7,500 per intentional violation |
“Both laws aim to protect consumer privacy, GDPR generally has stricter enforcement and a broader scope.”
Comparison report by the law firm DLA Piper
Does the CCPA Override HIPAA?
CCPA targets a different form of data than HIPAA, which focuses on protecting sensitive patients’ health information. HIPAA regulates issues related to protecting healthcare data, while CCPA focuses on the general protection of personal information.
CCPA does not override HIPAA, and there are situations where both laws can apply. For example, a healthcare provider subject to HIPAA is not exempt from CCPA if they are involved in activities outside the scope of healthcare data.
While CCPA concerns personal data and consumer rights, HIPAA deals with specific types of data related to patients’ unique needs.
“HIPAA remains the primary regulation for healthcare data, while the CCPA applies to broader consumer data.”
According to the Office for Civil Rights
How Does the CCPA Affect Cookie Usage?
The CCPA has implications for how businesses handle cookies and other tracking technologies. Under the Act,
- Businesses are required to disclose their use of cookies in their privacy policies.
- Consumers must be provided with the option to opt-out of the sale of their data, including information collected through cookies.
- While the CCPA does not require explicit consent for cookies like the GDPR, it requires businesses to communicate their data practices and provide users with options.
“Businesses are increasingly updating cookie policies and consent mechanisms to comply with the CCPA.“
Forrester Research
CCPA Compliance Strategies
Effective CCPA compliance requires a strategic approach that addresses multiple aspects of data privacy and protection.
Conducting a CCPA Assessment
- Map out where personal information is collected, processed, and stored.
- Use the assessment to identify any gaps in your current practices that may need to meet CCPA standards.
Developing a Comprehensive Privacy Policy
- Use a CCPA Privacy Policy Generator to explain clearly what data is collected and why.
- Ensure the privacy policy aligns with CCPA audit requirements and is easy to find and understand on your website.
- Update the policy regularly to reflect changes in your data practices or CCPA requirements.
Implementing Data Subject Access Requests (DSARs)
- Make sure you can verify the identity of anyone who makes a request.
- Respond to requests within the CCPA’s 45-day deadline.
- Consider using online portals to manage DSARs efficiently.
Managing Third-Party Relationships
- Add CCPA-specific clauses to contracts with vendors and partners.
- Regularly check that third parties adhere to CCPA standards.
- Ensure third parties don’t misuse or improperly sell shared data.
Employee Training and Awareness
- Educate employees on CCPA requirements and their role in compliance.
- Promote a culture of privacy across the organisation.
- Customise training to match the specific roles and responsibilities of each employee.
Data Security and Breach Notification
- Implement and maintain strong data security practices.
- Develop a clear plan to notify individuals affected by a data breach promptly.
- Outline steps to reduce damage and prevent future breaches.
“Businesses that invest in comprehensive data mapping and privacy notice updates position themselves better for compliance.”
The International Association of Privacy Professionals (IAPP) survey
CCPA Statistics
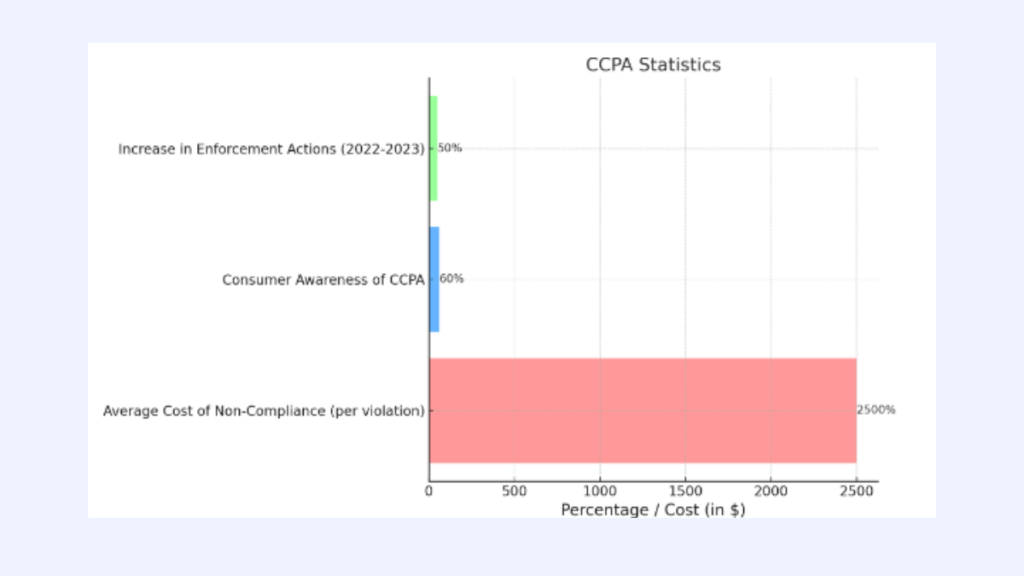
The chart reveals that the average cost of CCPA non-compliance is $2,500 per violation. Thus, non-compliance is a costly venture that businesses cannot afford.
Further, the survey revealed that 60% of Californian consumers are nowadays aware of the CCPA and their rights. Thus, the increasing number of consumers exercising their rights and demanding data may lead to more complaints.
The chart also shows a 50% increase in CCPA enforcement actions from 2022 to 2023, indicating that regulatory bodies are increasingly vigilant about holding non-compliant companies accountable.
Recent CCPA News and Trends
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is rapidly evolving, with recent legislative updates and a stronger focus on enforcement. The introduction of the California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA) has expanded the CCPA by establishing the California Privacy Protection Agency (CPPA) to enforce data privacy laws.
Remedial actions have become more aggressive. In particular, the California Attorney General’s Office tends to issue more violation letters.
Approximately 75% of businesses have corrected issues within 30 days of notification, highlighting the law’s growing impact.
CCPA Enforcement and Non-Compliance Penalties
Businesses that don’t comply with the CCPA can face hefty fines, with penalties reaching up to $2,500 for unintentional violations and $7,500 for intentional ones.
In some cases, consumers can also seek damages, adding to the risks for non-compliant companies. If a business doesn’t correct issues within 30 days of notification, regulators can impose fines of up to $7,500 per violation.
For serious data breaches, fines could reach millions, depending on the number of people affected.
Bottom Line:
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) enhances privacy rights for California residents, giving them control over their personal data and requiring businesses to be transparent about data use. Key rights include data access, deletion, and opting out of sales. CCPA compliance involves updating privacy policies and managing data practices effectively.
Use this information to make sure that you protect yourself against fines. Become compliant with CCPA Audit using the Seers CCPA Compliant Cookie Consent Management Solution.
Time to Secure Your Data
With Seers, you can
- Simplify compliance
- Protect your brand
- Boost conversions

Our expert-built solution offers
- Customisable banners
- Data privacy guidance
- Ongoing support
