The GDPR data protection principles set specific requirements and expectations regarding the safety and security of personal data. However, many organisations need help implementing a workable strategy to ensure compliance with GDPR law.
The GDPR stipulates some fundamental data protection principles, which should apply to all organisations and businesses that collect, store, and use personal data, regardless of size.
If you need clarification on the fundamental GDPR data protection principles, this guide can help you develop your understanding.
Importance of the Principles
- The principles are at the heart of the UK GDPR, laying the foundation for all the following rules and regulations.
- They don’t set strict rules but represent the core values of data protection, with very few exceptions.
- Following these principles is essential for good data protection practices.
- Complying with these principles ensures you meet the detailed requirements of the UK GDPR.
- If you don’t follow these principles, you could face severe penalties:
- Breaking the basic rules for handling personal data can lead to the highest fines.
- These fines can be up to £17.5 million or 4% of your total annual worldwide turnover, whichever is higher.
8 data protection principles
There are 8 data protection principles under GDPR that companies need to abide by to ensure compliance:
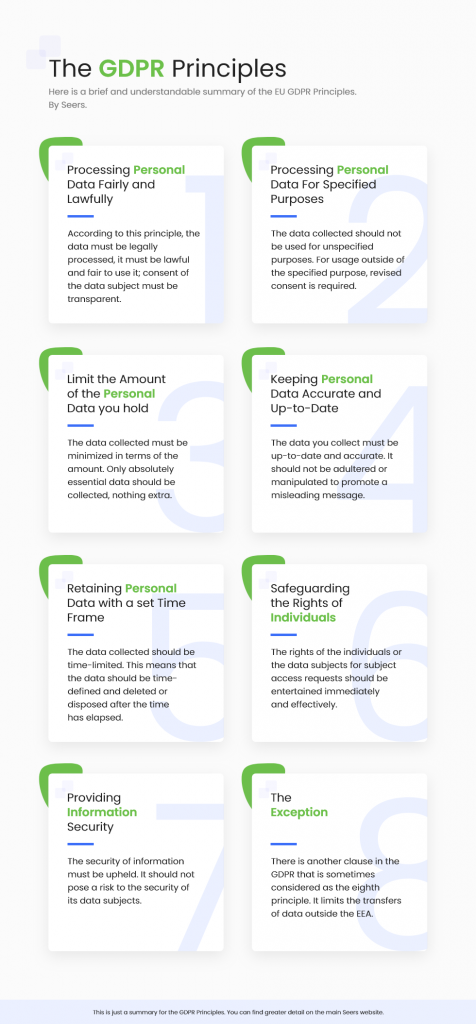
Principle 1: Lawfulness, Fairness, and Transparency:
The focus is on managing personal data. The best practice for organisations is to tell people before getting personal data.
“All organisations need to have strict policies and procedures in place to deal with data information requests by individuals and to be able to provide such information in an easy-to-understand way.”
Each of the DPA principles is essential for smooth compliance and lawful use of personal information—the fair, lawful processing of personal data is one of the key aspects of these principles.
Principle 2: Purpose Limitation
Organisations need a clear policy for collecting personal data. Personal information should only be collected with the person’s explicit consent and used for the requested reasons.
Principle 3: Data Minimization
Many organisations collect and hold enormous amounts of data for various purposes, such as monitoring behaviour, marketing, or research. Data may often be sensitive.
Many organisations collect and hold enormous amounts of data for various purposes, such as monitoring behaviour, marketing, or research. Data may often be sensitive.
The principle advises that organisations need to evaluate the relevance of the data stored.
Principle 4: Accurate And Up-To-Date
Organisations must have a comprehensive policy and procedure for regular reviews to ensure compliance with GDPR. All personnel should maintain an accurate database of all customer and employee personal information.
Principle 5: Storage Limitation
This principle states that data should only be kept for as long as necessary for the specific purpose for which it was collected. Organisations must carefully manage personal data storage, maintenance, and transfer to follow this rule.
Principle 6: Individual Rights
The GDPR Principles have expanded the rights of individuals to include:
- It is essential to know what sort of data organisations are collecting.
- How are organisations collecting data?
- What will organisations do with this data?
- How the Organizations now must provide, upon request, a copy of the data in electronic format, free of charge for portability.
Furthermore, the right to erasure gives the individual more choice over how their data is used or preserved.
Organisations must focus on policies and procedures to ensure that all staff members know the stages of request handling and ensure GDPR compliance.
The rights of the individual and their sanctity in the shape of a transparent flow of information are essential as one of the data protection principles.
Principle 7: Information Security and Integrity
There is no excuse for protecting and securing personal data and individuals’ privacy rights. Security measures are imperative in implementing this principle.
- Firstly, keep only the required data.
- Keep policies and procedures up to date and in line with the requirements,
- Educate and provide basic eight principles of GDPR-related training to all personnel accordingly
- Ensure all physical areas, hardware, and software have security and protection.
Principle 8: Accountability
Under this principle, organisations must ensure they are not sending personal data from the EEA.
There is a list of acceptable countries, but they do not include the US.
Countries that lack adequate levels of protection and appropriate safeguards, such as China, Japan, Brazil, and the Middle East, will need to ensure that they implement appropriate data privacy measures, such as the obtaining of explicit and informed consent or specific and approved contracts with guarantees through Model Contract Clauses.
Other legal methods of transferring personal data include Binding Corporate Rules, which allow multinational organisations to transfer data outside the EEA.
Summary of the 8 Key Principles of GDPR Data Protection
The 8 fundamental data protection principles under GDPR ensure a clear and transparent process. This enables a level of protection and security for individuals and provides a checklist and methodology for organisations to assist with compliance. Therefore, safeguarding the individual should be at the forefront of any business that collects, stores, and manages personal data.
Ensuring compliance with the GDPR Principles is an obligation. Upholding the principles entails upholding them in action and thought.
“The compliance to the GDPR law requires the use of best practices in the industry. It ensures that the data being processed, collected, stored and used is lawful, fair and transparent. There are data minimisation policies in place. All the collection and categorisation of personal data is accurate.“
Additionally, the business collecting personal data must maintain appropriate privacy protection. It is accountable to the data subjects, law enforcement, and regulatory bodies involved in its data collection, storage, and use phases.
However, this should sum up the 8 data protection principles explained in detail above under the GDPR.
So, the eight key data protection principles of GDPR are upheld through proper GDPR compliance training and using an artificial intelligence-powered tool kit that can help throughout the process.