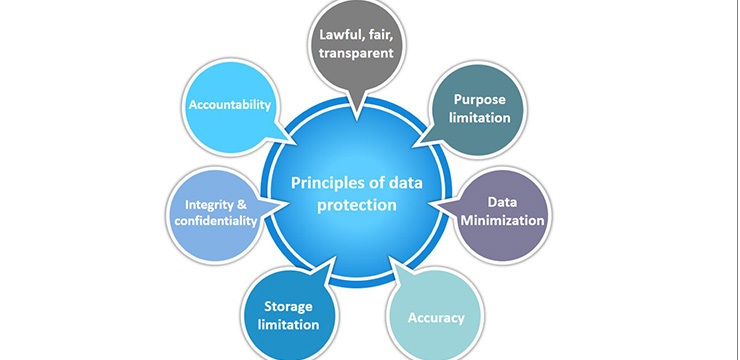
The General Data Protection Regulation is based upon seven data protection principles for the correct and lawful personal data processing on the internet. Processing includes collecting, organising, structuring, storing, altering, consulting, using, communicating, combining, restricting, deleting, or destroying.
The seven principles ruling personal data are;
- Lawfulness, transparency, and fairness
- Limiting purposes
- Minimising data
- Accuracy
- Limiting storage
- Confidentiality and integrity
- Accountability
The Data Controllers are also accountable for their processing. They must demonstrate their GDPR compliance.
The data should be processed fairly, lawfully, and in a transparent manner in relation to the individuals.
Data collection is only for explicit, legitimate, and specified purposes. Consequently, it should not be further processed in any way or manner that is incompatible with those originally stated purposes. On the other hand, further processing for the purposes of archiving on behalf of the public interest, as well as historical or scientific research purposes, and also statistical purposes, aren’t considered incompatible with those initial purposes.
Data processing should be relevant, limited to what is necessary, and adequate in relation to the processing purposes.
Personal data collection should be accurate. Moreover, data updation is very important. All reasonable steps are to ensure that all inaccurate personal data, regarding their processing purposes, are immediately rectified.
On one hand, personal data must retain in a personally identifiable form for as little time as possible. On the other hand, you can store personal data for longer periods only if the process is taking place for archiving purposes for the public interest, historical or scientific research purposes or other statistical purposes that are subject to implementing the appropriate organisational and technical measures as per GDPR requirement to safeguard the freedoms and rights of individuals.
In conclusion, data processing must go in such a way that it ensures proper personal data security. Besides, that includes the protection against unlawful or unauthorised processing and against accidental damage, loss, or destruction.