Are you overwhelmed by GDPR compliance? Are the legal terms and regulations leaving you confused?
You’re not alone. Many businesses, whether small or large, find it challenging to navigate these complex requirements.
But here’s the good news: we’re here to make it simple. Creating a clear, GDPR-compliant privacy policy doesn’t have to be a headache.
In this article, you will come across many elements of a GDPR policy template, learn what your privacy policy should include, where to post it, and how to simplify the process with an easy-to-use template.
total control of your legal policies and compliance
obligations under GDPR.
What is GDPR and Why Does it Matter?
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a crucial law designed to protect the personal data of individuals within the EU. It applies to any business worldwide that processes data of EU citizens.
Providing consumers with transparent and accessible information regarding their personal data is a legal obligation on companies under GDPR. One clear way to do so is to have a comprehensive privacy policy as well as all the other key policies and documents that are required to become compliant using GDPR policy template.
What’s Inside a Privacy Policy That Complies with the GDPR?
In order to ensure GDPR compliance, companies have had to give some thought and handle things more diligently in relation to data protection and privacy. Here’s what you need to include in the GDPR privacy policy:
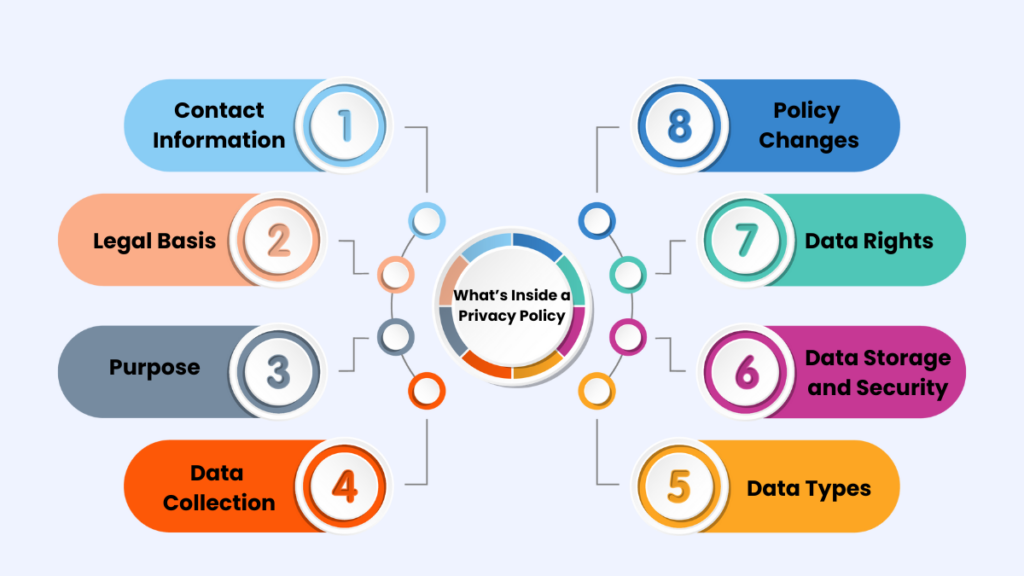
Contact Information
Users should know who to contact if they have questions about their data. If you have one, it should include your business name, address, and the contact details of your Data Protection Officer (DPO).
Legal Basis
Be transparent about why you’re processing personal data. Are you doing it with consent, for a contract, or because of a legal obligation? Let your users know.
Purpose
Clearly state the reasons why you’re collecting data. Is it for marketing, improving services, or fulfilling orders? Whatever the purpose, spell it out in simple terms.
Data Collection, Use, and Transfer
Your business should explain how it collects data, what it does with it, and whether it shares it with third parties.
Data Types
The user must know what types of information you are collecting. This might include user names, email addresses, phone numbers, IP addresses, and genetic data. Knowing what’s being collected helps users understand what’s being collected.
Data Storage and Security
Explain where you store the data and how long you keep it. Explain the security measures you’ve implemented to protect user data. Users want to know their information is safe.
Data Rights
The GDPR grants individuals various rights concerning their personal data. Users can access, correct, delete, or move their data. Your policy should tell users how they can exercise these rights.
Policy Changes
Let your users know that the business privacy policy might change and how you’ll inform them of these changes. This will keep everything transparent and help maintain trust.
Where to Post Your GDPR Privacy Policy
Having a well-crafted privacy policy is essential for GDPR compliance. But it’s equally important to ensure your users can easily find it. Here’s where you should post it:
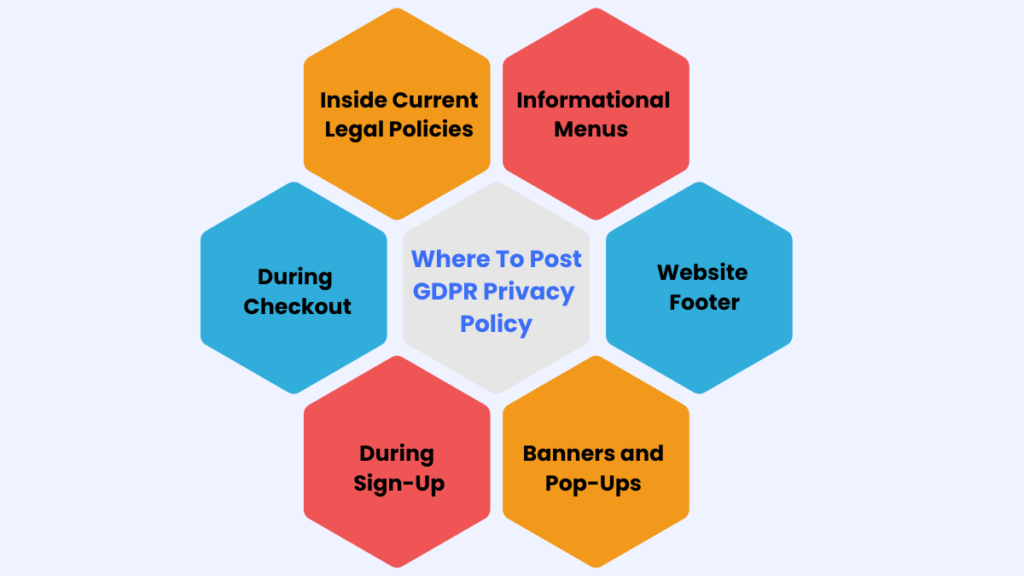
Inside Current Legal Policies
Integrate your GDPR policy into existing legal documents like terms and conditions. This keeps everything in one place.
Informational Menus or Sections
Add a link to your privacy policy in the informational sections of your website. Make it easy for users to find.
Website Footer
The footer is prime real estate for important links. Include your privacy policy here so it’s visible on every page.
Banners and Pop-Ups
If you want consent, use banners or pop-ups to notify users about your privacy policy. This is especially important when you’re collecting consent for cookies.
During Sign-Up
Display your privacy policy during the sign-up process. This ensures users are aware of it before they share their personal information.
During Checkout
For e-commerce sites, make sure the privacy policy is visible during checkout. This builds trust and shows transparency.
How to Create a GDPR Policy Template
A privacy policy is an important way to ensure compliance with a key GDPR principle regarding transparency. A compliant privacy policy must cover:
![]()
-
- It must be written in a simple language so your users can easily understand it.
-
- It must be comprehensive, which means it covers every aspect of your personal data processing activities.
-
- It must be easily accessible, particularly prior to the point that you’re collecting your users’ data or soon after if you’ve received it from elsewhere. However, you should update your privacy policy, whenever there are changes to the processing activities, in order to show compliance with GDPR.
Using Automated Tools
No need to start from scratch. Use Seers’ GDPR Policy Generator, which covers all the legal bases. You can generate a customised policy tailored to your specific needs with just a few clicks.
Legal Considerations
While our tool provides a solid foundation, it’s essential to consult with a legal professional for a comprehensive review. This ensures your policy addresses all relevant aspects of your business and remains compliant with the latest GDPR regulations.
Benefits of Using a GDPR Policy Template
Why use a template? Here are a few reasons:
Efficiency and Compliance
When you have a good template aligned with the GDPR rules, you will save considerable time that could be spent looking for potential points to address.
Consistency Across Operations
Standard data protection protocols are easier to implement when everyone in your business uses the same policy.
Good Examples of GDPR-Compliant Privacy Policies
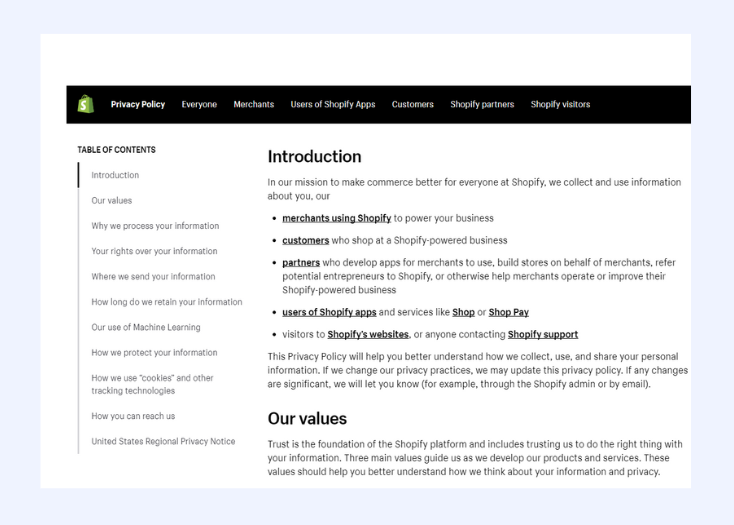
Shopify Privacy Policy
Shopify’s privacy policy is well organised and easy to understand, even for non-technical users. It covers all necessary aspects of data collection, use, sharing, and security.
The policy avoids legal jargon and uses plain language that is accessible to a broad audience. Shopify provides a clear and prominent cookie banner to obtain user consent for data collection.
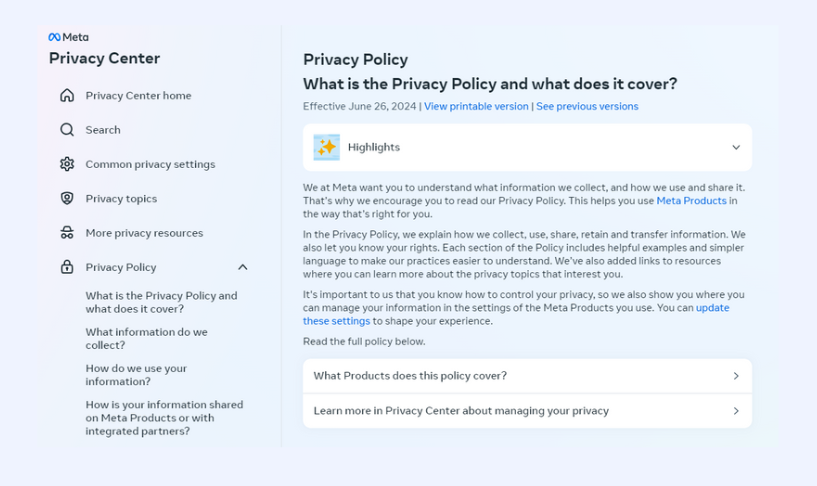
Meta Privacy Policy
Meta’s privacy policy stands out for its clear organisation and user-friendly design. The policy features a well-structured table of contents on the left side, allowing for quick navigation through different sections.
Additionally, Meta provides the policy in multiple formats, including detailed text and short explanatory videos, making it easy for users to understand the key aspects of data protection and privacy.
Implementing and Maintaining GDPR Compliance
Creating a GDPR policy is just the first step. Here’s how to keep it relevant and effective:
Regular Audits and Reviews
A privacy policy should be reviewed periodically to meet the evolving needs of a business or new regulation. This will ensure that you are always up-to-date and in compliance.
Policy Distribution
Ensure your policy is accessible to all stakeholders, from customers to employees. The more visible it is, the better.
Ongoing Employee Training
Your employees are on the front lines of data protection. In this way, they know what requirements of GDPR exist and how they can be met in their practice.
Conclusion
You might think GDPR compliance is a big issue, but in reality, it is not very difficult to comply with GDPR if you have the tools and proper guidance. Applying a GDPR policy template enables you to work quickly, avoid falling into a non-compliance trap, and gain customers’ trust. Ready to get started? Visit Seers today and download your template to reduce stress in your compliance process.
Seers offers comprehensive GDPR compliance solutions, including ready-made templates that you can customise to fit your needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can you write your own privacy policy?
If you do not have the means to write a privacy policy yourself, there are tools such as the Seers policy generator that can help you create a tailored policy that is appropriate for your business. Do not just use a privacy policy template from the internet, as the policies should be specific.
Do I need a GDPR policy template?
GDPR requires you to inform your consumers about how you are handling their personal data. So, if GDPR applies to you, then you must have a GDPR privacy policy.
Do I need a lawyer to draft a privacy policy?
No, it is not essential for the lawyer to draft your terms of use and privacy policy for your app or website. You can also utilise a policy generator to produce these documents for your business.

