Today, how a firm handles private information. This is the most essential part of its privacy policy how they take care of their private information is meant to be stored and kept confidential, even from other employees. Any environment where sensitive information is being gathered, maintained, or sent can risk sensitive data exposure.
This includes e-commerce transactions, healthcare systems, financial organisations, and other settings. When the sensitive source is made accessible, unauthorised people might use it for nasty objectives like identity theft, financial fraud, or other types of cybercrime.
In this article, we will discuss key points about sensitive data exposure, including what it is, how it differs from a data breach, 12 common causes of data exposure, examples, potential impacts, and 12 effective ways to enhance your sensitive data security in 2024.
Define sensitive data exposure.
“When unauthorised parties try to gain access to personal information by using false means, we can say that security vulnerability is known as “sensitive data exposure.”
Sensitive data includes a wide range of information, from personally identifiable information (PII) to confidential business. Protecting against cyber threats to sensitive data is crucial for maintaining its security.
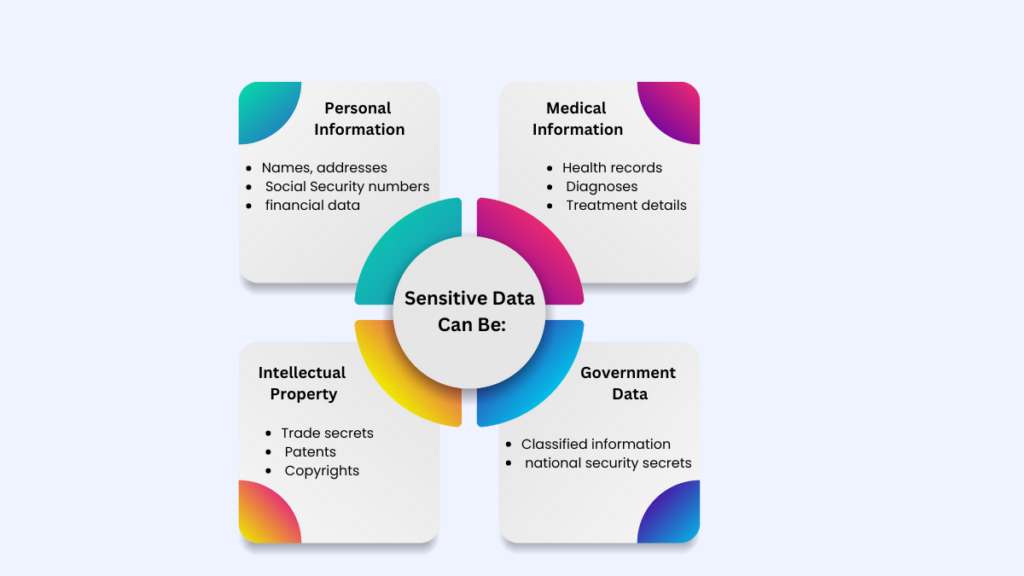
Today, it is the most essential part of any firm’s privacy policy how they take care of their private information, which is meant to be stored and kept confidential even from other employees. Any environment where sensitive information is being gathered, kept, or sent can have a risk of sensitive data exposure vulnerability.
This includes e-commerce transactions, healthcare systems(HIPPA), financial organisations, and other settings. When the sensitive source is made accessible, unauthorised people might use it for nasty objectives like identity theft, financial fraud, or other types of cybercrime.
Sensitive Data Exposure Examples
To understand the severity of sensitive data exposure, consider these real-world examples:
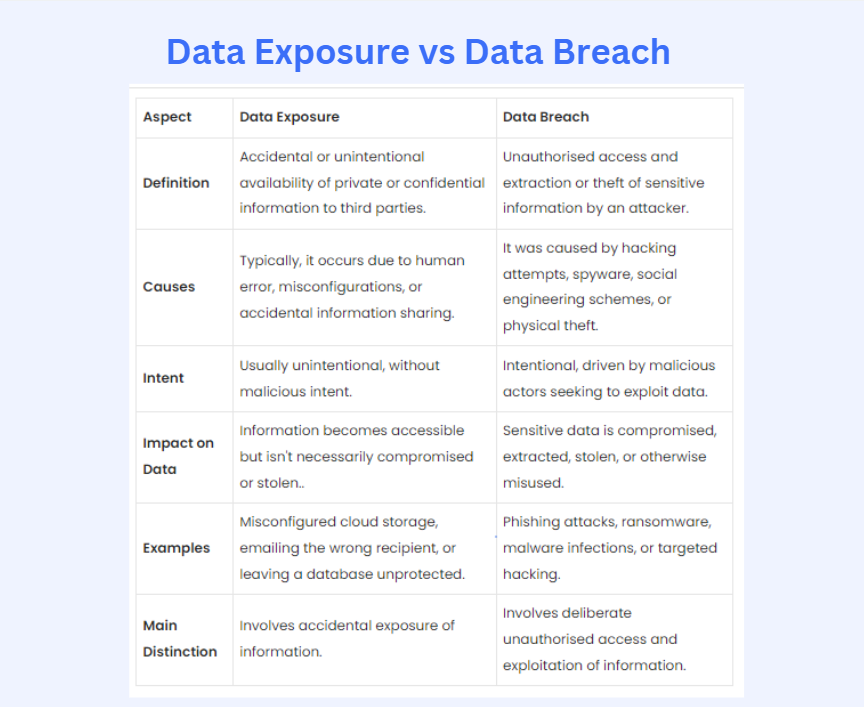
Difference Between Data Exposure and Data Breach
Why Is Sensitive Data Exposure a Major Concern?
Sensitive data exposure is more than just a technical issue; it’s a business risk with far-reaching consequences. Sensitive data exposure can lead to severe consequences, including:
Top 4 Internal Causes of Sensitive Data Exposure
Data exposure can occur through various means, highlighting the importance of adhering to data security best practices to avoid situations that resemble data breaches.
The primary reason behind the leakage of data is due to the following reasons:
1. Weak Passwords
Using easily guessable passwords or failing to update passwords regularly increases the risk of unauthorised access to sensitive information. The 2023 DBIR found that 82% of breaches involved a human element, with weak passwords being a significant factor.
2. Unencrypted Data
Storing confidential information in plain text rather than encrypting it makes it easier for unauthorised users to access and exploit that data. To prevent unauthorised access and exploitation, protecting personal data online with encryption is a fundamental security practice that many organisations still overlook.
3. Poor Access Controls
Increasing the number of people with access to sensitive information without proper need-to-know limitation raises the chances of inadvertent disclosure. Introducing role-based access controls (RBAC) will help minimise this probability.
4. Misconfigured Cloud Storage
As more companies move to cloud-based solutions, misconfigured cloud storage has become a leading cause of data exposure. A 2022 report by Check Point Research found that 93% of cloud deployments are misconfigured, potentially exposing sensitive data.
8 External Causes of Data Exposure Attacks
Several types of cyberattacks can lead to the exposure of sensitive data:
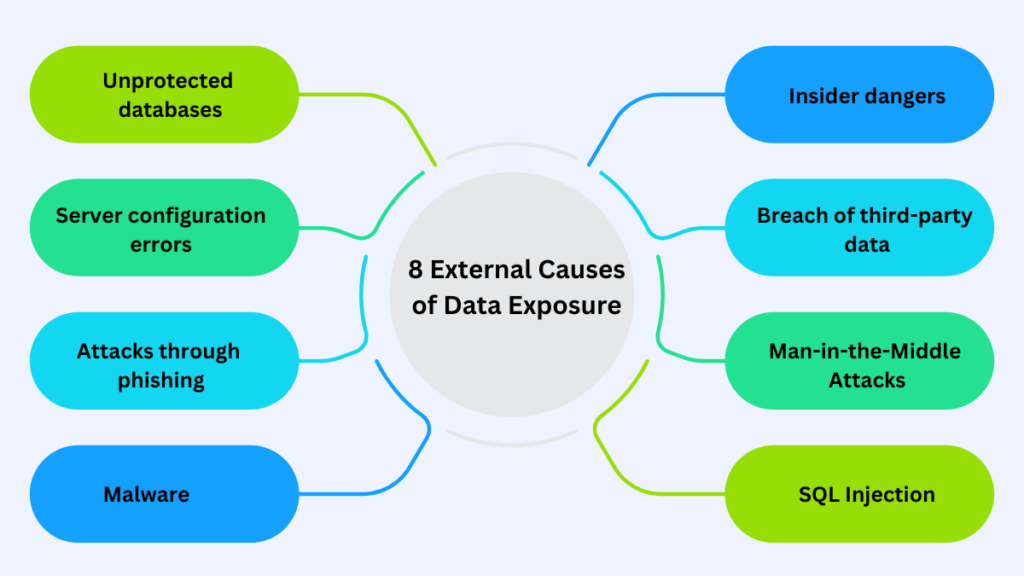
1. Unprotected databases
If databases are not adequately secured, sensitive data stored in them, such as financial and personal data, may be exposed. Attackers may access the database using weak or default credentials or taking advantage of the database software’s flaws.
2. Server configuration errors
Confidential and sensitive information may be made available to the Internet by servers that are improperly configured. If a server is configured to permit directory listing, an attacker can quickly navigate through the directories to uncover sensitive information.
3. Attacks through phishing
Attackers frequently use phishing scams to lure users into disclosing their login information. After a user’s account has been compromised, an attacker can access any private data kept there.
4. Malware
Malware can steal private information from a victim’s computer. For instance, ransomware can encrypt sensitive data and demand money to decrypt it, or a keylogger can record login credentials as they are input.
5. Insider dangers
Employees or contractors who have access to sensitive sources and unintentionally or intentionally reveal them are referred to as insider threats. This might happen due to inexperience, carelessness, or deliberate purpose. Proper data exposure risk management is essential to address these risks.
6. Breach of third-party data
When an attacker gains access to a third-party system that holds the data, the data might get exposed through a third-party data breach. A payment processor, for instance, might experience a security breach, exposing client payment information to attackers.
7. Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
In these attacks, a hacker intercepts communication between two parties, gaining access to the transmitted data. Securing confidential information is a key to maintaining privacy, attackers can easily steal sensitive information like passwords or credit card numbers without encryption.
8. SQL Injection
Attackers exploit vulnerabilities in an application’s code to access its database and retrieve sensitive data. SQL injection remains a common attack vector, with the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) listing it among the top 10 most critical web application security risks in 2024.
How GDPR Links to Data Exposure
GDPR staff training helps guide the company’s members to be well-educated about the General Data Privacy Rules and reluctant to expose themselves to data. Similarly, Seers keeps its employees well aware of market affairs related to the cookie consent banner, which provokes the new requirement to help its customers have a stress-free work experience.
12 Best Practices to prevent Sensitive Data Exposure
There are several ways to save yourself or your company from data exposure. Some precautions are more likely to reduce the risk of exposure, but one has to keep looking for new updates and versions to stay up-to-date in data protection compliance.
We define preventing data breaches as taking suitable measures before any fancy data tampering issues. We have discussed self-prevention and firm protection tips for data vulnerability. Seers provides its customers with the experience of prevention from excessive data exposure.
1. Cataloging Data
Organisations must maintain a comprehensive record of all data stored in their systems to protect customer information. Conduct regular audits to clearly understand data ownership, storage locations, security measures, and governance protocols.
2. Assessing Data-Related Risks
Organisations should evaluate the sensitivity of their data and allocate resources accordingly for risk mitigation. Highly sensitive data, even in small amounts, can pose significant threats if compromised.
3. Implementing Appropriate Security Controls
Organisations must establish robust security controls for data leakage protection to minimise the impact on individuals if exposure does occur
4. Taking Immediate Action
Organisations must have a well-prepared response plan to quickly address the exposure of sensitive information. Swift action is vital for data exposure prevention and to mitigate further damage.
5. Assessment and Proof of Concept (POC) for Sensitive Data Exposure
An essential step in preventing data exposure is conducting a thorough assessment of application security. Cybersecurity teams often use a proof-of-concept (POC) exploit to simulate attacks and identify vulnerabilities. If the team breaches the system, they identify potential risks that need addressing before malicious actors can exploit them.
6. Penetration Testing
Penetration testing involves security teams simulating attacks on an application to find any weaknesses. This approach gives valuable information about how well the application can defend itself, but it requires expertise and can take a lot of time.Penetration tests are done later in the development process, which can lead to increased costs and delays.
7. Legacy Application Security Scanning
Organisations often supplement penetration testing with legacy tools like Static Application Security Testing (SAST) and Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST). These tools identify vulnerabilities from an outside-in perspective. However, they have limitations, such as generating large volumes of false positives, requiring manual analysis, and struggling to assess API connections.
8. Web Application Firewalls (WAFs)
WAFs provide a perimeter defence against attacks by monitoring and filtering traffic to web applications. Organisations have used WAFs for decades, but configuring and managing them can be complex. They also generate numerous alerts, leading to potential fatigue among security teams and the risk of missing actual vulnerabilities.
9. Security Instrumentation for Continuous Protection
A more effective approach for sensitive information protection is embedding protection within the software itself. This inside-out approach, through tools like Interactive Application Security Testing (IAST) and Runtime Application Self-Protection (RASP), provides continuous monitoring from development through production. These methods reduce false positives, eliminate missed vulnerabilities, and streamline development.
10. Assessing Risks Related to Data Onboarding
Onboarding data and access rights are critical to introducing exposure risks. By thoroughly assessing these risks and continually monitoring changes, organisations can implement strict access controls to protect critical by thoroughly evaluating these risks and continuously monitoring changes assets.
11. Minimising Data Surface Area
Overprovisioning and excessive data sharing can complicate security efforts. Organisations should adopt a minimalistic approach, especially when dealing with sensitive information like health data or user credentials. Reducing the data attack surface helps mitigate the risk of leaks, particularly in cloud environments.
12. Using Salted Hashing and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for Passwords
Securing databases and services relies on robust password protection. Organisations should use advanced hashing algorithms and multi-factor authentication (MFA) to prevent unauthorised access to sensitive data.
Conclusion:
Sensitive information disclosure can be serious trouble for companies that don’t pay attention to privacy protocols. It has the capacity to destroy not only companies but also individuals. For a company to maintain its flow, it is mandatory to focus on ways to minimise the risk of exposure in any suitable way.
Data exposure can have significant consequences, including potential financial loss, reputational harm, and legal repercussions. By implementing strong measures for cybersecurity for sensitive data and preparing a detailed sensitive data breach response plan, organisations can reduce the risks of data disclosure.
How Seers Can Help Prevent Sensitive Data Exposure
Seers Overview:
- Seers offers comprehensive compliance solutions designed to protect your business from the risks of sensitive data exposure. Here’s how Seers can help:
GDPR and CCPA Compliance Tools:
- Seers offers compliance tools tailored for GDPR and CCPA regulations.
- These tools ensure that sensitive data is managed securely.
- They help your business stay legally compliant with data protection laws.
Data Mapping and Audits:
- Seers provides data mapping solutions to identify where sensitive information is stored.
- Regular audits powered by Seers detect potential vulnerabilities.
- These audits help prevent breaches before they occur.
Employee Training Programs
- Seers offers training modules to educate staff on best practices for data protection.
- The training reduces the risk of accidental data exposure by employees.
- It ensures that staff are up-to-date on the latest data security protocols.
Consent Management Platform
- Seers’ platform manages user consent for data collection, storage, and processing.
- It helps reduce the risk of unauthorised data access.
- Ensures compliance with privacy regulations by securing proper user consent.
Want to see how we Protect your data?
Book A Demo Now
