GDPR audit
A GDPR audit finds the key risks and gaps in an organisation’s processes, procedures, and policies under the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). It suggests ways to fix these gaps and reduce risks. This includes keeping an eye on personal data, stopping data breaches, training staff on GDPR rules, doing Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIA) for high-risk projects, following GDPR rules for getting consent and handling data subject access requests (DSAR).

Key benefits
-
- Raising data protection awareness.
-
- Documenting management’s commitment to recognising the value of data protection.
-
- Independent assurance of data protection policies, processes and practices.
-
- Indication of data protection risks with specific suggestions to automate compliance.
-
- Knowledge sharing for training and improvements.
Understanding GDPR Compliance
To fully grasp how to comply with GDPR, it’s essential to understand its core principles and the specific responsibilities assigned to data controllers and processors.
8 Principles of GDPR
There are 8 data protection principles under GDPR that companies need to abide by to ensure compliance:
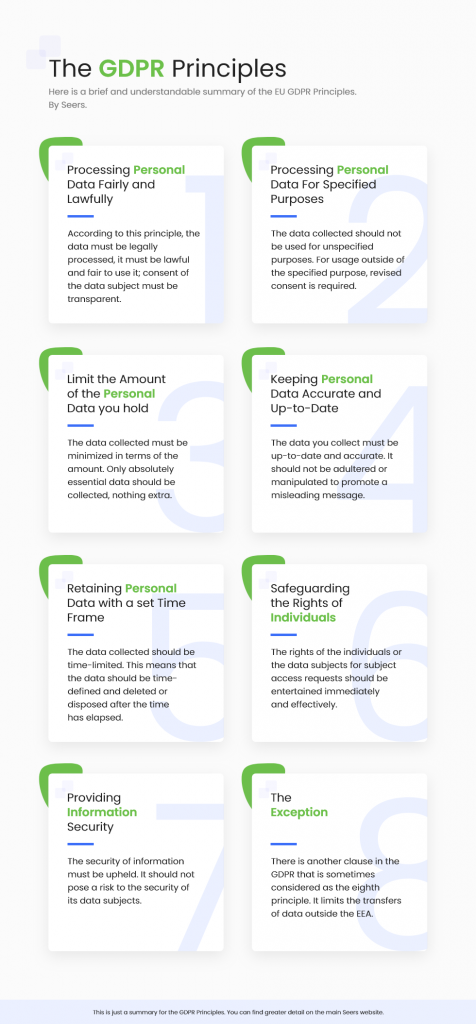
-
- Lawfulness, fairness and transparency
-
- Purpose limitation
-
- Data minimisation
-
- Accuracy
-
- Storage limitation
-
- Individual Rights
-
- Information Security and Integrity
-
- Accountability
Requirements for Data Controllers and Processors
Understanding the following responsibilities is crucial to ensuring that data controllers and processors meet GDPR requirements and protect personal data effectively.
Data Controllers
Data controllers decide how and why personal data is used. Their responsibilities include:
-
- Ensuring GDPR Compliance: Data processing activities must follow GDPR rules.
-
- Managing Data Subject Requests: Handle requests from individuals about their personal data, like access or deletion requests.
-
- Maintaining Records: Keep accurate records of how personal data is processed and used.
Data Processors
Data processors work with personal data on behalf of data controllers. Their duties include:
-
- Following Instructions: They must process data only according to the controller’s instructions.
-
- Implementing Security Measures: They must protect the data with proper security practices.
-
- Assisting with GDPR Obligations: They help the controller meet GDPR requirements.
-
- Having a Written Contract: Ensure contracts with data processors outline their responsibilities and duties, which can influence the overall GDPR audit cost.
Lawful Bases For Processing
The legal basis for processing personal data is mentioned under Article 6 of the GDPR, which must met by organisations.
-
- Consent: Ensure you have permission to process an individual’s data for a specific purpose.
- Contract: This is the processing required for a deal you shared with that particular individual. The reason is their consent to take specific steps before signing the contract.
- Legal obligation: Processing is necessary to comply with the law.
- Vital interests: This processing is crucial to shield someone’s life.
- Public task: This step should be taken when performing a task in the public interest. It is also vital for official functions, and the task should have a clear basis in law.
- Legitimate interests: The processing is imperative for the third party’s legitimate interests.
However, per the GDPR audit, there is a condition unless you find a rational reason to protect the individual’s personal data that precedes those legitimate interests.
What data are protected by GDPR?
Privacy policies apply to sensitive and private information, such as
-
- Bank details
-
- Name
-
- Address
-
- E-mail address
-
- Phone number
-
- Dates of birth
-
- Sexual orientation
-
- Religious beliefs
-
- Political views
What Do You Need to Carry Out a GDPR Compliance Audit?
To perform a GDPR compliance data audit, you need the following:
-
- Know Your Data: Understand what personal data you have, where it’s stored, and why you have it. Check if it meets GDPR standards.
-
- List of Third Parties: Your GDPR audit program requires you to include all external companies or organisations with which you share data.
-
- List of Data Access: Identify who in your organisation has access to personal data and define their roles.
-
- Data Processing Details: Know how you process the data and the reasons for processing it.
Is Your Business GDPR-Ready?
With Seers GDPR Audit, compliance has never been easier. Our Solution makes compliance easy so you can focus on what matters.
- Avoid penalties with a comprehensive audit.
- Keep your business compliant with up-to-date GDPR practices.
- Build trust with your audience by ensuring their data is safe.
- Fast, efficient, and hassle-free GDPR audits at your fingertips.
Don’t wait—ensure your business is GDPR-ready with Seers.
Start Your GDPR AuditEngagement with Legal Experts
Engaging with legal experts and GDPR auditors is essential for a comprehensive GDPR compliance audit. Legal professionals provide valuable insights, ensure solid GDPR efforts, and follow all rules. They can help spot potential problems and ensure your audit is thorough and legally correct.
Legal professionals provide crucial insights that help in understanding the intricate details of GDPR, ensuring no compliance aspects are overlooked.
According to legal expert Dr Emily Clark
Involving experts helps mitigate risks by addressing potential legal challenges early on, which can prevent costly compliance issues in the future.
Legal consultant Mark Johnson adds
Their specialised knowledge not only aids in navigating complex regulations but also in tailoring compliance strategies that are both effective and legally sound.
Attorney Rachel Adams emphasises
How to conduct a formal GDPR compliance audit
The initial stage in meeting GDPR audit requirements is familiarising yourself with the regulation’s obligations. Once you clearly understand what needs to be done, you can formulate a strategy and start making the required adjustments. You should appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO) to help ensure compliance.
To conduct a proper GDPR compliance audit, you will need to take several steps, including:
-
- Learn the Rules: Get to know what GDPR requires.
-
- Hire a DPO: Appoint a Data Protection Officer to help with the audit.
-
- Check Your Data: See your personal data and how you use it.
-
- Update Your Practices: Make necessary changes to how you handle data.
-
- Do Regular Audits: Review your data practices regularly.
-
- Include All Data: Look at all types of data in your organisation.
-
- Work with Third Parties: Check risks with any external service providers.
-
- Make a Plan: Create a strategy to ensure compliance.
-
- Train Your Team: Educate your staff about GDPR rules and data protection.
-
- Keep Records: Document your data processing and audit results.
-
- Consult Legal Experts: Get advice from legal professionals to address any issues.
How to Audit GDPR Compliance: A Comprehensive Checklist
A GDPR compliance audit checklist helps ensure your organisation follows the rules for protecting personal data. You can spot and fix any issues to keep up with GDPR standards by going through each item.
Data Inventory and Mapping
-
- Find your data: Determine what personal information you have and where you store it.
-
- Understanding how you use the data: Know why you collect it and how it is evaluated during a GDPR security audit.
Consent Management
-
- Be clear: Tell people what data you collect and why.
-
- Give choices: Let people decide if you can use their data.
-
- Keep records: Keep proof of people agreeing to you using their data.
Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs)
-
- Check for dangers: Look for activities that could harm people’s data.
-
- Manage risks: Find ways to reduce the risks to people’s data.
Data Security Measures
-
- Lock it up: Keep data safe from hackers with solid security.
-
- Check your partners: Ensure the companies you work with protect data.
-
- Have a plan: Know what to do if something terrible happens to your data.
Third-Party Contracts and Data Processing Agreements
-
- Partner up: Make sure contracts with third parties who handle data follow data protection rules like GDPR
-
- Have clear agreements: Write down what everyone’s responsibilities are.
Data Subject Rights and Requests
-
- Help people: If someone wants to see or change their data, help them.
-
- Delete data: If someone wants their data deleted, do it.
-
- Say no to selling data: Let people stop you from selling their information.
Breach Notification and Response
-
- Have a plan: Know what to do if something goes wrong with people’s data.
-
- Tell people if there’s a problem: Let people know if their data is at risk.
Record-Keeping and Documentation
-
- Write it down: Record everything you do with people’s data.
-
- Review regularly: Check your records to ensure you follow the rules.
Identifying and Addressing Non-Compliance Issues
When you find it, addressing the compliance issues quickly and effectively is essential. This section shows you how to find problems, plan fixes, and make changes.
Common Areas of Non-Compliance
-
- Data Handling Problems: Mistakes in how you manage personal data.
-
- Consent Issues: This needs to be clarified, or consent must be added from people.
-
- Security Weaknesses: Poor protection that can lead to data breach.
-
- Record-Keeping Mistakes: Not keeping proper records of data processing activities
Developing a Remediation Plan
-
- Find the Problems: Look at what went wrong.
-
- Plan the Fixes: Decide how to solve each issue.
-
- Set Deadlines: Decide when each fix should be done.
Implementing Corrective Actions
-
- Make the Changes: Apply the fixes you planned.
-
- Check Progress: Monitor to ensure the changes are working.
-
- Keep Records: Document what you did to fix the issues.
How Often Should a GDPR Compliance Audit Be Conducted?
Regularly reviewing your data protection audit is like getting a health checkup for your business. It helps you spot problems early on.
How Often Should You Audit?
Audits should be conducted as often as needed with the help of a data protection auditor, but they are recommended to be performed at least once a year.
You should then perform a GDPR compliance audit at least once a year. This is always helpful, especially when ensuring the organisation complies with the GDPR requirements.
When Might You Need More Audits?
-
- Changes in Data Handling: Do more audits if you start handling data differently or change how you use it.
-
- New Rules: Do extra audits if new GDPR rules or updates come out.
Tips for Scheduling and Doing Audits
-
- Plan in Advance: Set up a regular schedule for audits.
-
- Be Flexible: Adjust your audit schedule if there are significant changes in your data practices or new regulations.
-
- Keep Records: To keep track of your progress, note the details from each audit.
Continuous Improvement and Monitoring
Continuing efforts are crucial for maintaining GDPR compliance. Update your practices regularly and train your team to stay compliant and protect personal data effectively.
Keep Up with Compliance
-
- Review Regularly: Regularly check and update your data protection practices.
-
- Monitor Regularly: Make sure everything you do with data stays compliant with GDPR.
Train and Inform Your Team
-
- Offer Training: Teach your staff about GDPR rules and data protection regularly.
-
- Raise Awareness: Keep reminding everyone about data protection and GDPR updates.
Bottom Line:
In Conclusion, GDPR compliance is not only a legal requirement but also a business opportunity for your organisation. Auditing should be carried out per standard at specific intervals to identify risks and data protection issues and sustain your consumers’ trust in your organisation.
At Seers, we help you navigate GDPR requirements and provide your company with enterprise solutions. Contact us today to plan for GDPR compliance and enhance overall protection and compliance with regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Who can conduct a GDPR compliance audit?
An internal team with GDPR expertise or external consultants specialising in data protection and GDPR compliance can conduct a GDPR compliance audit.
What is a Data Protection Audit?
A Data Protection Audit systematically reviews an organisation’s data processing activities to ensure compliance with data protection laws and regulations, such as GDPR. It involves assessing data collection, storage, usage, and sharing practices to identify and address potential risks and protect personal data.
What is the Data Protection Act?
The Data Protection Act governs the processing of personal data in the UK. It aims to protect individuals’ privacy by regulating how organisations collect, store, and use personal information.

