Are you ready to advance to earning consumer trust in a $123.8 trillion US market?
The USA market creates opportunities for new businesses and supports existing companies in many ways.
However, compliance with CCPA and CPRA is essential in such a gigantic market. Noncompliance with California’s privacy laws may cause you and your business hefty fines.
You must know the CCPA and CPRA regulations to protect your operations and let these laws work to your advantage.
This blog will help you understand the differences between CCPA vs CPRA.
The Evolution of Consumer Privacy in California: From CCPA to CPRA
Before the CCPA vs. CPRA battle, let’s examine their evaluation and impact on consumers and businesses.
Chapter 1: The Birth of the CCPA (2018)
California is always considered the most advanced state and stays at the forefront regarding progressive consumer rights.
With the growth of digital technology and many blessings, the world faces many problems, including data privacy.
Many events where users experienced traumatic situations created the need for CPRA law.
California stood up for its residents by providing them with a magic wand called CCPA to control their data.
CA Consumer Privacy Act was a bold step that granted California residents their first rights over their data: the right to know, delete, and opt out of data sales.
For the first time, consumers could demand transparency. Depending on individual businesses, some may be slightly shaken, and others may try to manipulate the situation to move fully or partially along with the change.
Chapter 2: The CPRA Emerges (2020)
However, the CCPA did not end there. With more and more users entering the digital world, it was time for more advanced and extensive rules to cover the missing pieces in CCPA.
It was in 2020 that the California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA) was born, providing consumers with more potent tools and details than the original law. CPRA compliance requirements filled the gap in CCPA.
It cannot be termed simply an update; instead, it must be called a revolution.
The Act is as follows: it includes the right to correct incorrect information and allows customers to control the use of sensitive information. It was a significant change.
Offers not just deleting but rather managing others for clients to reaccess them. Many businesses that believed aligning with privacy under the CCPA would require no further change to their systems woke up and found reality hard at work. This reinforces CPRA as a champion for data subject rights.
Chapter 3: A New Enforcer Steps In
The CCPA first relied on the California Attorney General’s office to enforce its rules. However, due to the increasing complexity of the law, CPRA brought another agency onto the scene, namely, the California Privacy Protection Agency(CPPA).
The CPPA used to focus solely on enforcement and first relied on the California Attorney General’s office to enforce its privacy rules. It has also given powers to audit businesses.
It can impose fines. It can even guide to a more complete compliance.
Where the CCPA granted businesses warning signs, the CPRA gave them hard deadlines and enforcement mechanisms.
Such an ecosystem, which was created, meant that privacy would no longer be a good practice but made mandatory.
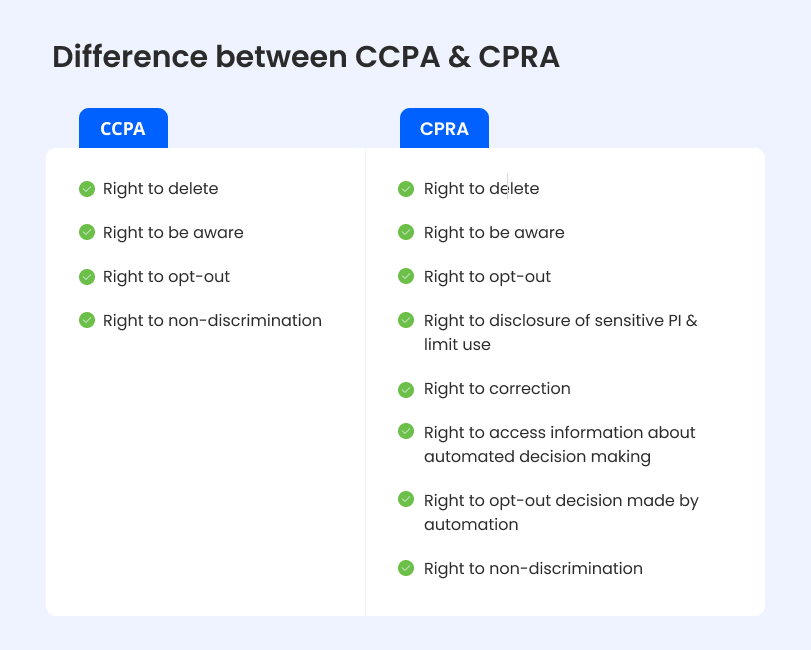
CCPA vs CPRA
Let’s compare CCPA vs CPRA so you can easily understand the differences without delving into complicated legal jargon.
Chapter 1: The Power Shift – New Rights for Consumers
The legal framework upon which rights of consumer privacy stand is known as the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), which enables residents of the state to access or delete their data and to opt out of their data selling.
On the contrary, when comparing CCPA vs CPRA, the latter had much more to offer, such as additional and new rights. It has also instituted correction rights over inaccurate personal information. As such, consumers can ensure that the information maintained by businesses about them is up-to-date.
Chapter 2: Sensitive Information – More Protection
Under CCPA, the most important aspect was not concerning sensitive personal information that contains biometric data or social security numbers.
Businesses could freely collect, use, and sell the information without much ado. Well, everything has changed with the CPRA.
Under CPRA, further classification was added to define sensitive personal data, including health data, sexual orientations, and even the extent of precise locations.
More recently, businesses must also provide a mechanism to enable customers to opt out of sharing sensitive information. Thus, it will be better secured in the most sensitive areas.
See here for everything you need to know about Sensitive personal information under the CPRA.
Chapter 3: Data Retention – How Long Is Too Long?
The California Consumer Privacy Act was one of the first pieces of privacy legislation. However, it offered no guidance on how long a company could retain your information.
The California Privacy Rights Act now requires businesses to disclose the retention policies for specific data types.
Additionally, businesses can only hold data for as long as it is necessary to complete the purpose for which it was collected; those who retain data longer than required will face possible consequences.
Therefore, if a business has stored your data for no reason, you now have the right to command to delete it.
Chapter 4: Enter the CPPA – A New Agency to Enforce Privacy
The essence of laws is that they only thrive without implementation. Therefore, while the CCPA brings significant power without it, the CPPA bears powers that are not associated elsewhere.
Before the CPPA, the Attorney General is responsible for enforcing such privacy laws. However, the CPRA dictates that California must have a single-minded agency devoted to the mission.
Therefore, the CPPA is now the compliance-enforcing body that imposes and filifiles against violators. This entails close monitoring from an exceptional team so that the customers’ rights are not invaded.
Chapter 5: The Opt-Out Update – Beyond Just Sales
Consumers can always opt out of selling third-party data regarding their information under CCPA. Fair enough, right?
Before, the stakeholders had all the control over the information collected, whether selling it or sharing it.
Consumers will now be able to opt out of these privileges. That will change the game for many potential entities that could have used the data to advertise to different consumers.
This is a different kind of control data flow other than CCPA. Now, you can stop the information from being shared for targeted ads; thus, sharp in privacy is what this text reminds us of.
Chapter 6: Sharing vs. Selling – The New Definition
One of the CPRA’s alterations that knocked the ball from the park was the definition of data sharing under the Act.
Whereas CCPA had the same as selling data, businesses were earlier quick to find loopholes by sharing data with third parties to target advertising, among others.
To this California, said, “Not so fast!” Under CPRA, “sharing” data no less than selling such data requires consumers to have an opportunity to opt out of arguably privacy-invading data-sharing practices.
Chapter 7: Penalties- A Tougher Stance
This point is one of the significant differences between CCPA and CPRA. The penalties for infringement in the CCPA may not be penetrating compared to other degrees of punishment.
The law has penalties of up to $2,500 per infraction or $7,500 for knowing violations; however, with the passage of CPRA, the stakes get higher.
In this case, organisations will incur late penalties of as much as $7,500 for each infraction. Thus, organisations that handle sensitive data poorly now have even more excellent reasons to comply with the law, especially for the more vulnerable populations, such as children.
Chapter 8: Who’s Affected? The Growing Scope of Businesses
The CCPA marks a strong start in breadth and applies to any corporation with at least 50,000 consumers, households, or devices; however, CPRA ran further and fixed the new threshold to the level of 100,000 consumers or households.
This is worse because businesses that have never come within its scope due to their colossal volume of data will start to be drawn under the risk of California privacy through this expansion.
Today, we keep up-to-date with the mammoth volume of personal data companies produce in the tech and advertising world.
Chapter 9: The Road Ahead – A New Privacy Era
The CCPA was an outstanding feat, but the CPRA extends further to realise the maximisation of consumers’ rights over protecting their privacy.
The CPRA contains concrete directives on data sharing and severe penalties upon breach. It would deal with data privacy from more critical lenses.
From all appearances, California appears to be a consumer’s shield, and business players should be keen to cope with its stand or get crushed by it.
A Future of Stronger Privacy Protections
The transition from CCPA to CPRA goes beyond modernising laws; it balances the power between consumers and corporations.
The law was the basis of the CCPA. However, with CPRA, stakes are higher because privacy is declared a right and not a luxury in California.
Therefore, businesses have a lesson to learn: it is no longer an afterthought. Compliance is no longer an option with CPRA.
This is about trust, transparency, and ethical responsibility. It is the dawn of a new era for consumers to assume once again control over their private data while bringing data usage into line with their values.
CCPA/CPRA Compliance with Seers CMP
Compliance with data privacy regulations such as CCPA and CPRA is essential for businesses that collect, store, or share personal data today.
Seers CMP is a consent management platform that acts as a gateway to ensure your website complies with the above regulatory requirements and averts possible fines or reputational damages.
How Seers CMP Ensures Compliance
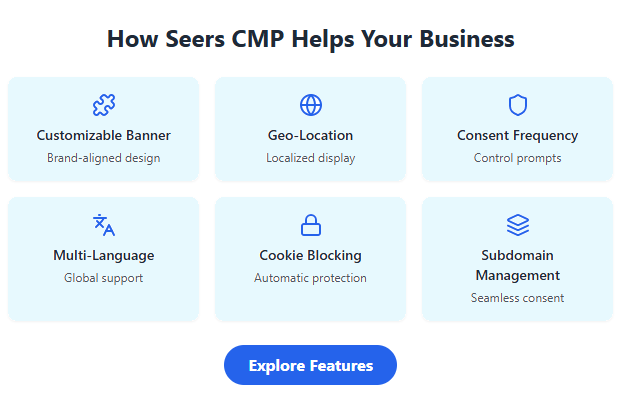
Seers CMP makes compliance with businesses’ websites with CCPA and CPRA easy. Here are the critical elements that make Seers CMP an ideal solution:
| Feature | Description |
| Customisable Cookie Banner | Design and personalize your cookie consent banner to fit your brand’s needs. |
| Geo-Location Detection | Automatically display a cookie banner in the appropriate language based on the user’s location. |
| Consent Frequency | Set how often users are prompted to give consent, complying with CPRA requirements. |
| Multi-Language Support | Display banners in multiple languages to cater to a global audience. |
| Cookie Blocking | Automatically block cookies until user consent is obtained. |
| Subdomain Support | Manage consent across multiple subdomains under a single Seers CMP account. |
Automated Cookie Consent Management
Seers CMP automatically blocks cookies, tags, and third-party trackers until users consent. CCPA/CPRA compliance requires explicit consent before businesses collect personal data through cookies or other tracking technologies.
Requests for User Data Access & Deletion
Seers CMP supports consumer rights under both CCPA and CPRA, enabling businesses to handle requests for data access, deletion, and correction efficiently, ensuring compliance with CPRA right to correct and other CPRA sensitive data rights.
Privacy Policy Generator
Again, CCPA/CPRA makes it mandatory for companies to change their privacy policies from time to time based on the kinds of personal information they collect and the purpose for which they collect such information.
With Seers CMP, businesses can do CCPA and CPRA privacy easily because a cookie policy generator helps them create and update privacy policies compliant with this regulation.
Consent Logs
Under both CCPA and CPRA, business parties shall maintain all user consents. The Seers CMP develops consent logs necessary for demonstrating that the particular business has indeed obtained the required approval of the users.
This is important in cases where California Privacy Protection Agency audits are being presented.
Integrations with Multiple Platforms
Seers CMP provides several flexible setups with many platforms for easy integration across companies of any size.
Seers integrates seamlessly with WordPress, Shopify, or any other CMS platform by ensuring they comply with CCPA and CPRA.
Why Seers CMP?
Seers CMP, a Google Consent Mode Partner, offers services like automatic blocking of third-party cookies and trackers, multi-site subdomain support, and a comprehensive cookie database to comply with PECR regulations.
Currently boasting close to 5,000+ companies worldwide, it is clear that this CMP solution is the one to go for if you are indeed looking for global privacy compliance.
Getting Seers CMP To Work
Steps to Getting Started with Seers CMP Simple steps: And get your website CCPA/CPRA compliant:
-
- Sign Up for Seers CMP and start with the free plan.
- Scan your website for tags, cookies, and trackers that may require user consent.
- Customise your consent banner to match your website’s design.
- Embed the Seers cookie notice script into your website.
- Start collecting consent from your visitors.
Ensure CCPA/CPRA compliance—Try Seers CMP free for 14 days and streamline your privacy management! .
Start your FREE TRIAL NOWFAQs
The California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA) is a state privacy law in California, USA, enacted in November 2020. It extends and enhances the privacy rights of California residents established under the California Consumer Privacy Act of 2018 (CCPA).
Opt-Out of Sale: California residents have the right to opt-out of the sale of their personal information by a business.
The CPRA and the CCPA are two different laws, therefore One difference between them is the definition of “personal information”. The CPRA expands the definition to include new categories. These new categories include geolocation data, biometric information, and internet or other electronic network activity information. In last examples of the latter category are browsing history and search history.
In conclusion, the California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA) protects the personal information of California residents. Personal information is defined broadly and includes any data that can directly or indirectly identify. A California resident or household, such as names, addresses, email addresses, phone numbers, and more.
Available Plugins Integrations
WordPress, Shopify, Drupal, Joomla, Magento, BigCommerce, Weebly, Prestashop