Implementing GDPR can be a very painstaking process as it involves kup to dated with shifting laws and maintaining compliance. One of the toughest challenges? Addressing how to manage the data breach. So, data owners or data protection officers’ (DPO) role plays an essential part as well – if breaches do happen, they still have to be ready how to manage this crisis.
This guide has been created to familiarise you with GDPR data breach management beginning from the scope of a data breach to the end of a breach response plan and recovery.
What is a Data Breach Under GDPR?
Under the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), a data breach is defined as any security incident that results in the unauthorised access, disclosure, alteration, or destruction of personal data. The GDPR breach management framework aims to ensure that organisations act promptly and effectively in response to such incidents.
Types of Data Breaches
Each breach type has a different procedure and consequences:
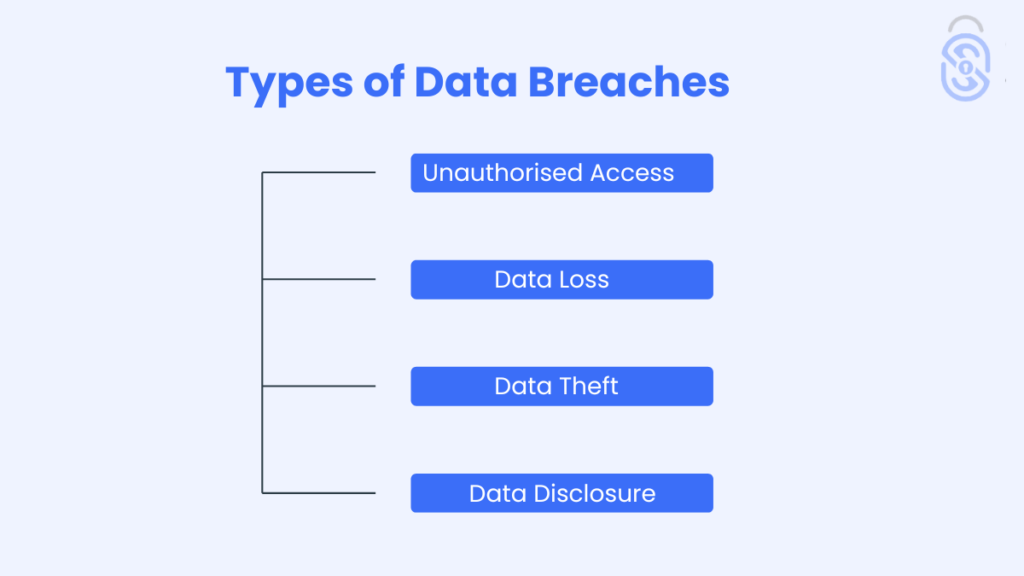
Unauthorised Access
This happens when someone gains access to personal data without a specific authority, which includes hacking or neglectence by the access rights allocators.
Data Loss
When there is accidental destruction, hardware malfunction, or corruption of business information. These are cases of possible loss of essential customer information, which can all affect business operations.
Data Theft
This is an attack in which information is collected and used to remove data from the organisation through means such as hacking or phishing, which is regrettable since this information may be misused.
Data Disclosure
This happens when unauthorised persons access to accessible information occurs accidentally for example a poorly directed email internal use where critical information is posted online.
Data Breach Examples
Imagine a situation in which your customer database has been hacked, and information such as names, mail addresses or even credit card numbers is in the hands of the criminals.
Or picturing an employee making a mistake which leads to e-mailing some members of the group with confidential customer details served the other members of the business.
Both are instances of GDPR data breaches that require immediate action.
Top GDPR Protocols for Data Breach Response
GDPR establishes particular rules for minimising data breaches in order to promote honesty and responsibility.
Article 33 GDPR
This article requires that organisations notify the relevant supervisory authority of a data breach within 72 hours of discovering it. The notification must include details of the breach, its impact, and the measures taken to address it.
Data Breach Notification
The organisation is unnecessarily delaying informing the affected individuals if it falls within the category of the criteria set forth as a breach with a high risk to their rights and freedom. The notice should be detailed about the incident, its consequences, and avoiding such consequences in the future.
GDPR 72-Hour Rule
Highlighting the importance of reporting breaches. Failure to report within the prescribed deadline may result in severe penalties and legal implications.
Your Action Plan When Facing a Data Breach
When dealing with a data breach, an organised strategy is needed to properly handle it.
- The first goal is to limit the intrusion and avoid future data loss. This may include isolating impacted systems, resetting passwords, or cancelling access.
- Determine the scope of the breach. What data was compromised, the severity of the harm, and whether any personal information was implicated?
- Report the breach to the relevant supervisory authority within 72 hours, as mandated by GDPR. Include all required details in your notification.
- Use a GDPR breach notification template to inform affected individuals. Clearly outline what happened, how it affects them, and what steps they should take.
- Conduct a post-breach audit to determine what went wrong. Revise your data security procedures and policies to plug any holes found during the intrusion.
Preventing Common GDPR Data Breach Errors
To prevent common pitfalls in GDPR data breach management:

- Delayed Reporting: To avoid fines and penalties, ensure that you disclose violations within 72 hours.
- Inadequate Communication: Provide clear and comprehensive information to affected individuals to maintain trust and transparency.
- Neglecting Post-Breach Analysis: Don’t overlook the importance of a post-breach audit. This is crucial for identifying weaknesses and preventing future incidents.
Tools for Effective GDPR Data Breach Management
Utilising the right tools can streamline your breach management process:
- Data Breach Prevention Software
- Data Breach Detection Tools
- Encryption Tools
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Solutions
These tools can help you to manage the
The Role of a DPO in Breach Management
A Data Protection Officer plays a pivotal role in GDPR breach management:
- Overseeing Breach Response: The DPO ensures that the response to a data breach aligns with GDPR requirements.
- Guiding Compliance: They provide advice on compliance and help navigate the regulatory landscape.
- Coordinating Notifications: The DPO is responsible for ensuring that all necessary notifications are made promptly and accurately.
Case Studies: Real-Life GDPR Data Breaches
Examining real-life GDPR data breaches can provide significant insights.

Fines & Penalties for GDPR Data Breaches
GDPR fines can be severe, with penalties reaching up to €20 million or 4% of global annual turnover, whichever is higher. These penalties highlight the need of strict data protection measures and timely breach response.
Adhering to your GDPR obligation requires immediate breach reporting and ensuring that all necessary precautions are in place to prevent potential violations and protect personal data.
How to Create a GDPR Data Breach Response Plan
A well-crafted response plan includes
Immediate Actions
Steps to contain and assess the breach, including isolating affected systems and changing access credentials.
Notification Procedures
Guidelines for notifying authorities and affected individuals, including timelines and required information.
Resilient Recovery Methods
Plans for addressing the breach’s impact, restoring normal operations, and enhancing security measures to prevent future incidents.
The Importance of Staff Training in Breach Management
Training staff on data protection and breach response is crucial
GDPR Training
Regular training ensures employees understand GDPR requirements and their role in data protection.
Building Cybersecurity Awareness
Educates staff on recognising and avoiding potential security threats, reducing the risk of breaches.
Post-Breach: Steps to Improve Security
After handling the immediate aftermath of a breach:
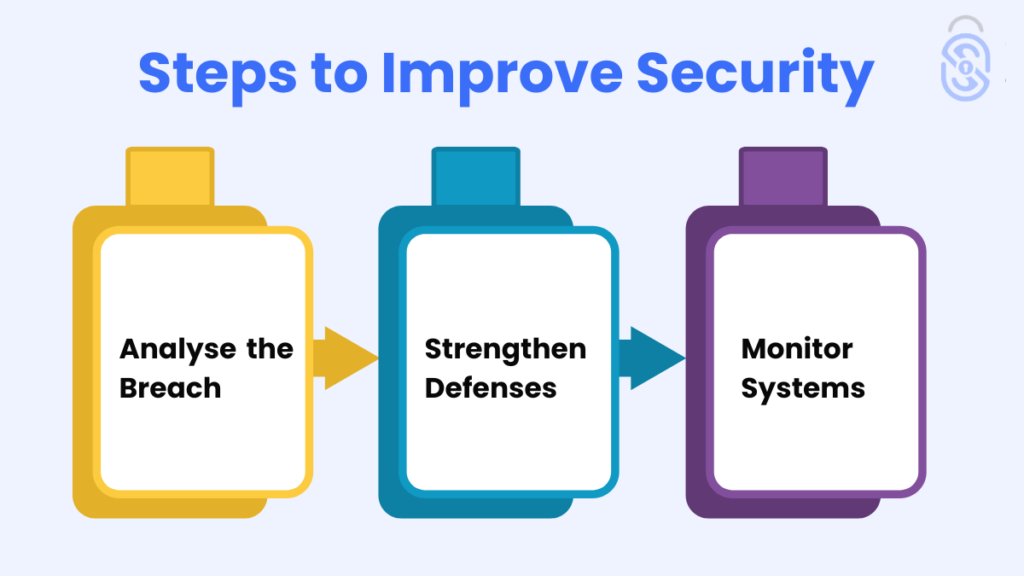
Analyse the Breach
Conduct a thorough analysis to identify how the breach occurred and what can be improved.
Strengthen Defenses
Implement stronger security measures such greater encryption, access limits, and frequent security audits.
Monitor Systems
Continuously monitor your systems to detect and address potential threats promptly.
How Seers Can Help You in Data Breach Management: GDPR Staff Training
Effective data breach management starts with a well-informed team. Seers offers comprehensive GDPR staff training designed to equip your employees with the knowledge and skills necessary to handle data breaches efficiently and comply with GDPR requirements.
Comprehensive GDPR Training
Provides essential knowledge on GDPR principles and breach management.
Practical Scenarios
Uses real-world examples to prepare staff for actual breach situations.
Ongoing Updates
Keep your team informed about the latest GDPR changes and best practices.
Customised Programs
Tailors training to fit your organisation’s specific needs and industry.
Faster Response
Equips staff to respond swiftly and effectively to data breaches.
Seers’ GDPR staff training ensures your team is prepared, compliant, and ready to handle data breaches efficiently.
Conclusion
Managing GDPR compliance and data breaches is a complex but crucial task. You can effectively handle breaches and minimise their impact by understanding GDPR requirements, implementing a robust response plan, and using the right tools.
Key steps include having a clear response strategy, promptly notifying relevant parties, and conducting post-breach analysis to improve security measures. The role of a Data Protection Officer is critical in ensuring compliance and guiding breach management.
Learning from real-life breaches and understanding potential penalties can reinforce your commitment to data protection. With vigilance and preparation, you can safeguard personal data and strengthen security.
