When it comes to online interactions, most of us have seen that small pop-up asking for our permission to use cookies. But have you ever stopped to think about the bigger picture behind it?
User permission is a cornerstone of legal and ethical business practices in today’s digital age, where privacy and security of personal information & data are of the utmost significance. When users give their OK to collect, process, and share their data, this is known as “user consent.”
This article will examine the meaning of user consent, describe the many forms consent may take, and provide suggestions for collecting and managing user consent in a way that complies with applicable laws and standards.
What is User Consent?
In simple terms, user consent is when a person gives permission for their data to be collected, processed, or shared. Whether clicking ‘accept’ on a cookie consent banner or agreeing to a privacy policy, the goal is the same: to let users decide how their personal information is used.
Organisations need user consent management to build trust, comply with data protection laws, and practice ethical data practices. Informed user consent is vital,it gives people ownership over their data and encourages data openness and accountability.
User permission lets people access, correct, or remove their personal data. Organisations may promote privacy and develop user trust by acquiring and honouring user permission.
Why is user consent necessary?
| Reason | Explanation |
| Respect for the Law | Data protection and privacy rules demand user consent. Whether you’re dealing with cookie consent or more extensive personal data, compliance with data protection laws like the GDPR and CCPA is non-negotiable. Noncompliance with these standards may result in serious fines and reputational harm. |
| Guarding Confidentiality | Protecting privacy requires user permission. By getting permission, firms promise to protect user privacy and use personal data only as agreed. Show them you respect their user privacy rights. |
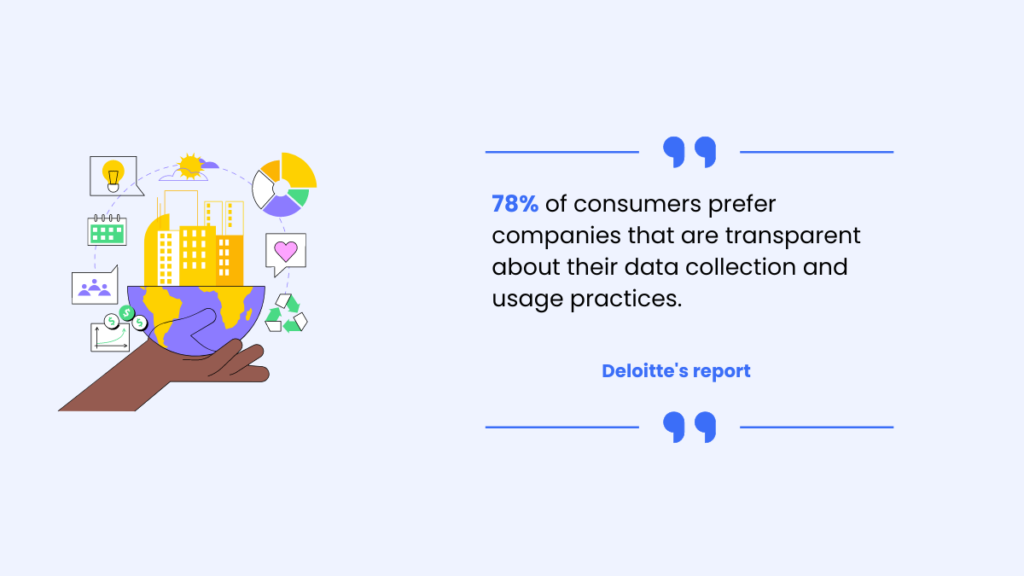
| Honesty and confidence | User permission improves data transparency. Transparent practises generate trust and beneficial user-organization connections. Being transparent helps build loyalty. |
| Customisation and User Interaction | Companies may customise services and experiences with user permission. For businesses, ensuring that users can easily opt-in or opt-out with well-placed options like a privacy consent banner builds trust. |
| Good Data Ethics | Consent shows data ethics. Responsible data management requires respecting user liberty and privacy. It fosters justice, accountability, and the appropriate use of personal data. |
| Risks to One’s Reputation and Legal Standing | Companies benefit from user consent. They may retain trust and reputation by prioritising user consent. Clear, accessible privacy policy consent and consent form compliance give users peace of mind. |
Are all privacy laws compliant with the user’s consent?
Many privacy laws emphasise user consent. However, some have different consent criteria. User consent definitions, circumstances, and exclusions vary by jurisdiction. Most privacy regulations require informed, voluntary consent from users to handle personal data.
Organisations must know and follow their local privacy legislation. This involves comprehending valid consent criteria, the extent of permission, and any extra concerns like age-specific consent for children. Privacy regulations require user permission but are not the sole legal basis for collecting personal data.
Depending on the circumstances and objectives of data processing, other legal grounds, such as the need for contract performance, compliance with legal duties, protection of vital interests, or the data controller’s legitimate interests, may apply.
Organisations should engage legal experts or privacy specialists to tailor their consent practices to privacy legislation. For instance, if a person claims that someone added me as an authorised user without my consent. Then, according to privacy laws, penalties will be imposed on that firm.
So, it is understandable that user consent is the most vital aspect, and all privacy laws are shaped according to it.
Types of user consent
Organisations may seek user permission based on data processing and privacy rules. The types of user content include;
Opt-in consent:
Opt-in consent requires affirmative action on the user’s part, such as checking a box or selecting. The user is in charge of the decision-making process and must act actively to show their approval.
Opt-out consent:
If a user does nothing to withdraw their consent actively, it will be assumed that they do consent. Unless the user actively unsubscribes, they will continue to receive marketing materials through this method.
Specific consent:
Consent that is “purpose-specific” pertains to a specific processing activity. By being required to express explicit permission for each processing purpose, individuals are afforded fine-grained control over the uses to which their data is put.
Broad consent:
A single permission request allows organisations to get approval for various processing actions and objectives. Clear and complete information regarding the various processing processes must be provided so that people can make educated decisions.
Explicit consent:
Explicit consent is the most potent permission form for sensitive personal data or specialised processing activities. It requires people to take visible and positive action to show that they are okay with having their data processed.
Implied consent:
Consent may be inferred from the user’s actions or behaviour. It’s the norm when asking for someone’s permission is implicit in their use of a service like a website or an app. If users see a cookie banner and continue browsing the site, they may be giving their tacit approval to install cookies on their devices.
Retrospective consent:
After data is collected or processed without permission, the data subject provides their consent retroactively. This entails obtaining authorisation after the fact, usually when adding novel processing activities or altering the original intentions for using the data.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
It’s not enough to have a cookie banner; it must be done right. Many businesses make the mistake of hiding the consent process behind walls of legalese or confusing pop-ups.
Keep things simple. Clear, concise language is your friend. And don’t forget to allow for granular control—users should be able to consent to specific data practices, like e-commerce cookie consent, rather than being forced into an all-or-nothing scenario.
Make sure your consent requests are visually appealing. A well-designed consent banner can ensure the process feels smooth and professional rather than intrusive.
What Should You Include in Your Consent Process?
Clear Language: Make sure users know exactly what they’re agreeing to. This means using simple words to explain how their data will be used, whether it’s for cookies or tracking tools.
Granular Options: Let users pick what they’re okay with. For example, they might want to accept essential cookies but not marketing ones. Giving users control over their choices is a key part of good user consent management.
Opt-In Options: An opt-in consent approach is crucial for cookie tracking consent or any other data collection method. Users should actively agree to tracking and data collection, not just be defaulted into it. Make sure they have to opt-in rather than opt-out.
Frequent Updates: Privacy laws change, and your consent methods should keep up. Ensure your consent mechanisms are always in line with the latest regulations, like updates to cookie policy compliance or data privacy compliance.
Easy Consent Withdrawal: Users should be able to change their minds and withdraw consent easily. Ensure there’s a simple way for them to do this so they don’t get frustrated and you stay compliant.
How to Implement User Consent Efficiently
Implementing user consent doesn’t have to be overwhelming. Here’s a roadmap for making the process smooth:
- Use a Consent Management Platform: These tools help you track and manage user consent, keeping you compliant with laws like GDPR and CCPA across different regions.
- Incorporate a Simple Consent Banner: keep your consent banners clear and easy to understand. Avoid complicated forms—simplicity is key.
- Make It Flexible: Allow users to choose their preferences for different types of data. Some might want only essential cookies, while others may accept tracking cookies. Flexibility ensures a better user experience.
How Do Companies Get the Consent of Users in Processing/Collecting Data?
Companies obtain user consent for data processing by implementing clear and transparent communication methods, such as detailed privacy policies and straightforward opt-in forms, as part of a comprehensive user consent authentication process. They allow consumers to agree to data processing through easy-to-understand channels, such as cookie banners and preference centres.
Companies are required to ensure consent is specific and recorded, complying with regulations such as the GDPR and CCPA. Effective communication allows users to understand and manage their consent.
Companies provide user-friendly interfaces that let users make informed decisions about data privacy; this enables companies to communicate clearly and collect information in a trusted manner.
How Can Seers Helps?
Using Seers, you can confidently prepare your business for legal requirements and develop trust with your users by creating transparent, respectful, and ethical data practices. Use Seers to find out more about what we can do to support your privacy and compliance priorities.
What Seers Brings to Your Business
Seers Overview:
- State-of-the-Art Cookie Consent Management: Our platform simplifies compliance with global privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA. With our flexible cookie banners and preference centres, users can easily choose what they accept or reject.
Founding Purpose:
- Seamless Compliance and Growth: Seers was created to help businesses effortlessly navigate the complexities of data privacy. Our solutions are designed to support both compliance and business growth.
Passion and Motivation:
- Commitment to Data Privacy: We are dedicated to helping businesses meet legal requirements while building user trust. Our mission is to offer reliable, effective solutions that enhance your brand's credibility and user confidence.
What We Offer:
- Customisable Banners: Tailor consent banners to fit your website’s design and functionality.
- Seamless Integration: Easy integration with your existing systems ensures a smooth user experience.
- Compliance Assurance: Tools and templates to help you maintain up-to-date privacy policies and legal documents.
- Partnership Opportunities: Explore how to work together to elevate your compliance strategy.
Want to see how Seers can transform your business?
Start Your Free Journey TodayConclusion:
Consent from users is essential for ethical data handling and protecting individual privacy. Businesses may improve trust, compliance with data protection rules, and user interactions by learning about user permission, the numerous forms of consent, and best practices for getting and managing consent.
Cookies issued without user consent have a severe penalty. User consent must be prioritised to guarantee ethical data practices, give users agency, and help create a safer and more transparent digital environment. Seers allow businesses to experience the healthy climate of the consent system.
Available Plugins Integrations
WordPress, Shopify, Drupal, Joomla, Magento, BigCommerce, Weebly, Prestashop